Acetyl Coa And Gluconeogenesis
When there is an excess of energy available gluconeogenesis is inhibited. In this way the cell makes sure that gluconeogenesis and TCA cycle will not happen simultaneously.

6 42 Gluconeogenesis Nutrition Flexbook
Gluconeogenesis

Gluconeogenesis Wikipedia
Within the liver proprionate serves as a major substrate for gluconeogenesis which is absolutely critical to the ruminant because almost no glucose reaches the small intestine for absorption.

Acetyl coa and gluconeogenesis. Acetyl-CoA levels back up and allosterically activate pyruvate carboxylase. LDH is found in almost every cell of the body. Thus fatty acid oxidation elevates ATP concentrations and the concentration of both acetyl-CoA and citrate.
Also notice that ATP is required for a biosynthesis sequence of gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors including pyruvate lactate glycerol and aminoacids In animals the gluconeogenesis pathway is for the most part the reverse of glycolysis. Oxaloacetate depletion hinders acetyl CoA entry into Krebs Cycle.
Gluconeogenesis begins in the mitochondria with the formation of oxaloacetate by the carboxylation of pyruvate. Conversion to acetyl-CoA by PDH for complete degradation or for synthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol Carboxylation to oxaloacetate for use in gluconeogenesis or in the citric acid cycle Synthesis of amino acids eg. Inhibition of pyruvate.
Organic Biochemistry Miscellaneous. Acetyl-CoA activates pyruvate carboxylase which converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate OAA for use in the gluconeogenic pathway. Acetyl-CoA is the indicator of cells metabolic activity and functions as a gluconeogenesis regulator at a local level.
More specifically pyruvate carboxylase is activated by acetyl-CoA. If the concentration of acetyl CoA is low and concentration of ATP is high then gluconeogenesis proceeds. It acts as allosteric activator of the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase and inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase of.
The six-carbon citrate molecule is systematically converted to a five-carbon molecule and then a four-carbon molecule ending with oxaloacetate the beginning of the cycle. This cycle allows the body to get energy from proteins carbohydrates and fats. Acetyl-CoA goes through the citric acid cycle and after oxidative phosphorylation produces 22 ATP per molecule.
Pyruvate is an important molecule that is present at the intersection of multiple biochemical pathways. The conversion of pyruvate to PEP is regulated by acetyl-CoA. Once carbohydrate stores become depleted and gluconeogenesis cannot occur anymore ketogenesis is substantially increased.
Acetone does not convert back to acetyl-CoA. It is important for the organism to conserve as much energy as possible. 37-1These vitamins are normally synthesized by microbes inhabiting.
In starvation there is excessive breakdown of fatty acids resulting in formation of Acetyl coA in liver. This enzyme is stimulated by high levels of acetyl-CoA produced in β-oxidation in the liver and inhibited by high levels of ADP and glucose. When energy is required gluconeogenesis is activated.
ATP acetyl-CoA and citrate are important effectors during gluconeogenesis. Oxaloacetate is an intermediate of the citric acid cycle where it reacts with acetyl-CoA to form citrate catalyzed by citrate synthase. This causes pyruvate to build up in cells.
Lactate dehydrogenase converts lactate to pyruvate for gluconeogenesis or for metabolism to acetyl-CoA Cori cycle in the liver. Elevated LDH levels without exercise may indicate cell injury due to cancer eg germ cell tumors hemolytic anemia myocardial infarction infection kidney or liver disease. In the absence of oxygen or when oxygen demand outstrips supply pyruvate can undergo fermentation to produce lactate.
Acetyl CoA is the entry point to the citric acid cycle and while acetyl CoA will be oxidized and CO 2 released this does not happen directly but occurs via an eight-step process. As each and every cell in the body needs energy glycolysis happens in all the cells and the location of glycolysis is the cytoplasmOwing to its inevitability glycolysis can occur both in the presence and in the absence of oxygen. When Gluconeogenesis is active in the liver oxaloacetate is diverted to form glucose via PEP.
The first step of the citric acid cycle is the transfer of two carbons from acetyl CoA to the 4-carbon sugar oxaloacetate to generate the 6-carbon sugar citrate - hence the name of the cycle. It is essentially a reversal of glycolysis with minor variations of alternative paths MDM00003. The process and where does glycolysis take place.
Acetyl coA in Gluconeogenesis. Introduction to the Study of Chemistry - Atoms Elements Compounds Chemical Properties Physical Properties. Proprionic acid is almost completely removed from portal blood by the liver.
This reaction also requires one molecule of ATP and is catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase. Entry of propionate into gluconeogenesis as well as amino acids that are converted to propionyl-CoA requires pantothenate a source of coenzyme ASH vitamin B 12 and biotin see Fig. Gluconeogenesis is a synthesis pathway of glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors.
The concentration of acetyl CoA and ATP determines the fate of oxaloacetic acid. They ensure the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetic acid. Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle by combining with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate to form the six-carbon molecule citrate or citric acid at the same time releasing the coenzyme A molecule.
There are substitute or bypass reactions for the irreversible steps of. Another important use of acetate is as the major source of acetyl CoA for synthesis of lipids. Gluconeogenese is het opnieuw vormen van glucoseBij gluconeogenese wordt glucose uit niet-koolhydraatbronnen als aminozuren en glycerol maar vooral uit pyrodruivenzuur gemaaktVerder kunnen naast pyrodruivenzuur ook glycerine di- of tricarbonzuren als uitgangsstof dienen.
It is commonly encountered as one of the end products of glycolysis which is then transported to the mitochondria for participating the citric acid cycle. When the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is not working properly pyruvate cant be converted to acetyl-CoA. It is also involved in gluconeogenesis the urea cycle the glyoxylate cycle amino acid synthesis and fatty acid synthesis.
Acetyl-CoA another important precursor metabolite is produced by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate. Acetyl-CoA is an important compound that helps the body make energy through a cycle known as the citric acid cycle. Acetyl CoA enters Krebs Cycle by condensing with oxaloacetate whose concentration tends to be limiting for Krebs Cycle.
De glycerine ook glycerol genaamd is van de afbraak van vetten afkomstig en de di- en tricarbonzuren van afbraak van.

Jci Insight Impaired Ketogenesis And Increased Acetyl Coa Oxidation Promote Hyperglycemia In Human Fatty Liver

Oxaloacetic Acid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
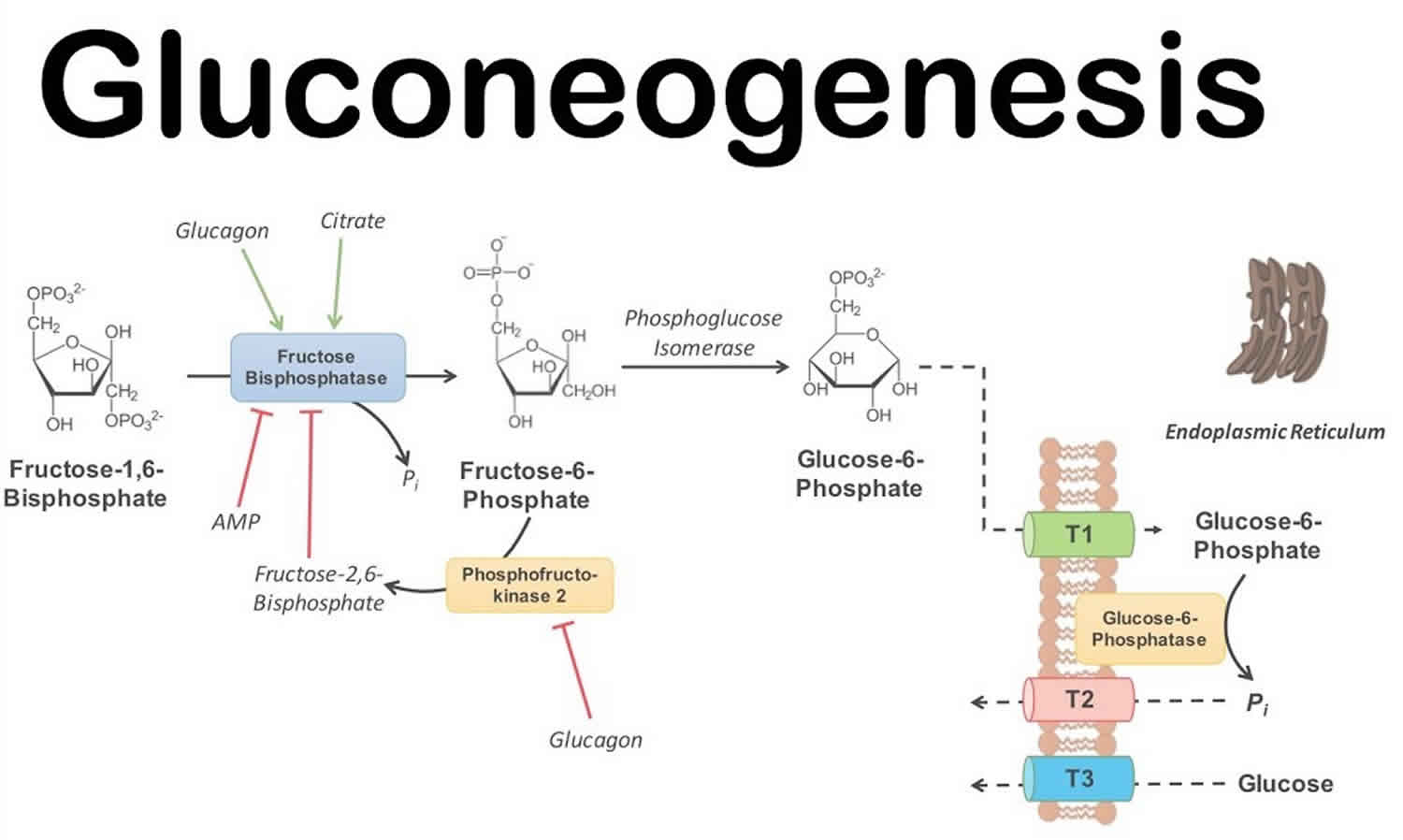
Gluconeogenesis Porcess Steps Pathway

Diagram For Citrate Metabolism And Bicarbonate Formatio Open I
Gluconeogenesis

Figure Gluconeogenesis Image Courtesy Dr Chaigasame Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
1
Plos Computational Biology In Silico Evidence For Gluconeogenesis From Fatty Acids In Humans
0 Response to "Acetyl Coa And Gluconeogenesis"
Post a Comment